Introduction to WebDNN¶
Recently, deep neural network (DNN) is attracting a lot of attention in various fields such as image and video recognition, natural language processing and gaming AI. In these fields, DNNs are applied for various products. However, DNNs are computationally expensive and generally hardware acceleration is required for its execution, and so it is not practical to execute DNN on end-user devices such as laptops or smartphones.
One of the solutions to this is cloud computing. As another solution, WebDNN highly optimizes the DNN models and executes them on the web browsers in end-user devices.
Key features of WebDNN are the follows.
- Installation-free
- Non overhead interface
- Inference-phase-specialized optimization
Installation-free¶
WebDNN executes DNN models on a web browser. Usually, web browsers are already installed on end-user devices already and users are familiar with how to use it. Therefore, using WebDNN, DNN applications can be provided easily, without any difficulty in installing a native application.
There are a few number of major web browsers, and they have different set of features that can be used for acceleration. WebDNN have several sterategies to execute DNN model as speedy as possible in each web browser.
Non overhead interface¶
JavaScript is a standard programing language running on web browsers. It is executed by an interpreter. Therefore, it requires computing overhead and it cannot completely harness the capacity of the CPU. The same problem is encountered in GPU. Modern web browsers support WebGL, which is a JavaScript API to use GPU. However, this API is designed for graphics processing and is not suitable for general purpose computation. In addition, using WebGL for general purpose computing incurs overhead costs.
WebDNN uses next generation JavaScript API, WebGPU for GPU execution, and WebAssembly for CPU execution. These APIs help to bring out the full performance of GPU and CPU.
Inference-phase-specialized optimization¶
To achieve speedier execution, optimizing the computation graph of DNN models is very important. Execution of DNN consists of two phases, the training phase and the inference phase, and they requires different optimization sterategies. WebDNN focuses on only the inference phase execution on end-user devices and supports aggressive optimization. This optimization pipeline can be applied for models trained with various DNN frameworks. It is not required to edit the training codes.
Framework structure¶
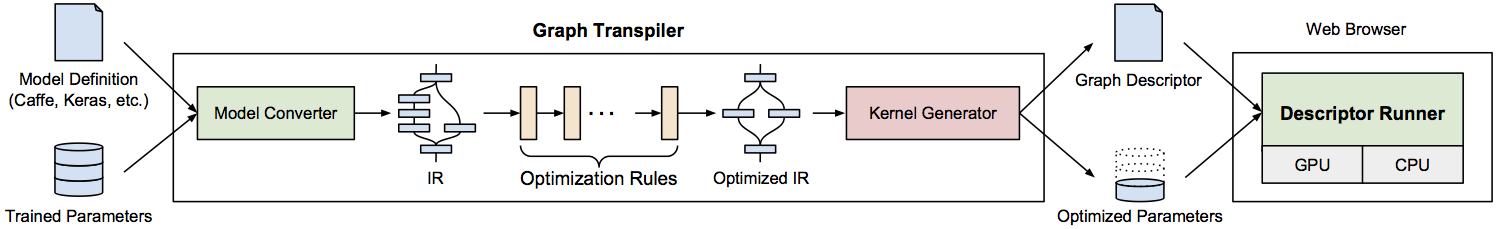
WebDNN consists of two modules - the graph transpiler, which transpiles and optimizes trained model into an executable format on the web browser and the descriptor runner, which executes the converted model on the web browser.
Graph transpiler is the offline module to transpile the model. It is implemented in python (version 3.6) and only application developers need to run it. It outputs the ‘graph descriptor’ files, which consist of JavaScript and binary weight data.
Descriptor runner is the online module to run the graph descriptor on the web browser of the end-users. It is JavaScript files. Application developers have to use the API provided by the library to supply input to the model and display output.
Setting up the application development environment is described in [setup](../setup.html) page. You can find examples of steps to use models from Caffe, Keras, Chainer in WebDNN in the example directory.