3. Layer with Weights¶
In this section, you will learn about how to convert custom keras layer which has trainable weights.
Complete sample code is included in /example/custom_operator/section3.
Example: Bias¶
In section 1 and section 2, we learned how to convert operators which have no weights.
In this section, we’ll consider BiasLayer defined as follows:
class BiasLayer(keras.layers.Layer):
"""
Trainable bias layer
# Input shape
2D tensor of shape `(num_samples, features)`.
# Output shape
2D tensor of shape `(num_samples, features)`.
"""
def build(self, input_shape):
self.bias = self.add_weight(name='bias',
shape=(input_shape[-1],),
initializer=keras.initializers.get("uniform"))
def call(self, x):
return x + self.bias
This layer has a trainable weight named "bias".
Axis and Order¶
To define variables and operations’ semantics, Axis and Order object is defined in WebDNN.
Axis¶
Axis object represents each dimension of tensors. Typical axes are pre-defined like follows:
Axis.N # batch size
Axis.C # number of features
Axis.H # height of image
Axis.W # width of image
Axis.T # length of series
For example, a tensor of shape (batch_size, features) is 2D tensor. This tensor’s first dimension is represented as
Axis.N, and second dimension is represented as Axis.C in WebDNN.
Also, Axis object is used to define operation. For example Softmax
operator is compute normalized exponential values. Generally, that values are normalized along to Axis.C.
Order¶
Order object represents the data order of variables. For example, the data order of a tensor of shape
(batch_size, features) is OrderNC.
WebDNN operators are designed to receive various data order. For example, generally
Softmax operator is used to normalize OrderNC variable
along to Axis.C and the output is also OrderNC variable. However WebDNN
Softmax operator can receives OrderCN variable too.
Typical order is defined in webdnn.graph.order.
Define Converter Handler¶
Based on previous section, Let’s convert BiasLayer.
Luckily, bias operator is already implemented in webdnn as ElementwiseAdd, or operator +. You only have to implement
converter handler. Converter handler is implemented like follows:
from webdnn.frontend.keras.converter import KerasConverter
@KerasConverter.register_handler("BiasLayer")
def square_converter_handler(converter, keras_layer):
keras_x = converter.get_input_tensor(keras_layer)[0]
webdnn_x = converter.get_variable(keras_x)
webdnn_b = converter.convert_to_constant_variable(keras_layer.bias, OrderC)
webdnn_y = webdnn_x + webdnn_b
keras_y = converter.get_output_tensor(keras_layer)[0]
converter.set_variable(keras_y, webdnn_y)
The important lines are follows:
webdnn_b = converter.convert_to_constant_variable(keras_layer.bias, OrderC)
converter.convert_to_constant_variable(weight, order) is the
function which converts keras weights into WebDNN variables. The output variables’ data order is determined by order. In
BiasLayer’s case, bias is a tensor of shape (features,). Therefore order=OrderC is specified.
Different from webdnn_x and webdnn_y, it’s not need to store webdnn_b into converter because
keras_layer.bias is not referenced from other keras layers.
Test¶
Let’s test the implementation.
# test.py
import bias
import keras
import numpy as np
from webdnn.backend.fallback.generator import FallbackDescriptorGenerator
from webdnn.backend.webassembly.generator import WebassemblyDescriptorGenerator
from webdnn.backend.webgpu.generator import WebGPUDescriptorGenerator
from webdnn.frontend.keras.converter import KerasConverter
# Define Keras model
x = keras.layers.Input((10,))
layer = bias.BiasLayer()
y = layer(x)
model = keras.models.Model([x], [y])
# For test, initialize bias by 100.
keras.backend.set_value(layer.bias, np.ones(layer.bias.shape) * 100)
# Convert Keras model into WebDNN graph IR
graph = KerasConverter(batch_size=1).convert(model)
# Generate graph descriptor
WebGPUDescriptorGenerator.generate(graph).save("./output")
WebassemblyDescriptorGenerator.generate(graph).save("./output")
FallbackDescriptorGenerator.generate(graph).save("./output")
<!--index.html-->
<button onclick="main()">RUN</button>
<script src="../../../dist/webdnn.js"></script>
<script type="application/javascript">
async function main() {
let runner = await WebDNN.load("./output");
let x = runner.inputs[0];
let y = runner.outputs[0];
x.set([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]);
await runner.run();
console.log(y.toActual());
}
</script>
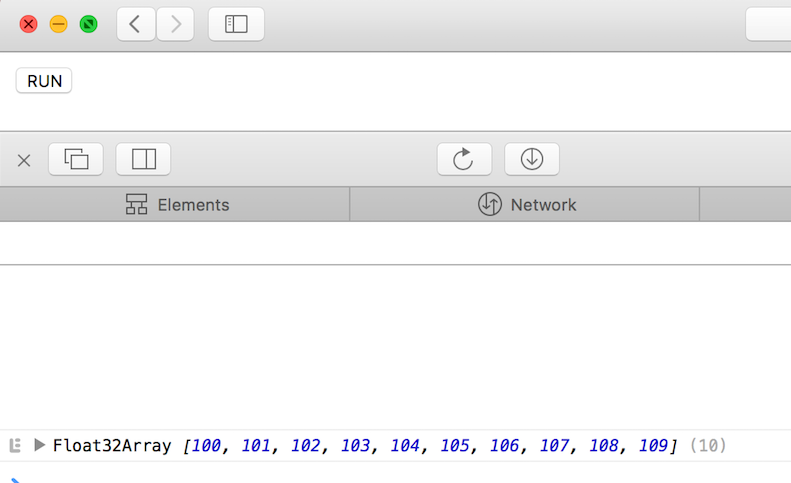
The result is like follows.